Internet of Things (IoT) : How IoT is Changing the World
Published: 21 Jun 2025
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing how we live and work. It connects everyday devices, allowing them to share data over the internet. For example, a smartwatch tracks your steps, or a smart thermostat automatically adjusts your home’s temperature.
With billions of devices connected worldwide, IoT makes life smarter and more convenient. It helps industries like healthcare and agriculture by turning data into useful insights, improving efficiency in many areas.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the Internet of Things (IoT) and its exciting possibilities for the future.
The Evolution of IoT
The journey of IoT started with basic connectivity. Early systems relied on simple machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, primarily in industrial settings. Over time, advancements in wireless networks, sensors, and data analytics brought IoT to the forefront.
Key milestones in IoT development:
- 1999: Kevin Ashton coins the term “Internet of Things.”
- 2008: The number of connected devices surpasses the global population.
- 2014–2020: Explosion of consumer IoT devices, from smart homes to wearables.
This evolution has led us to a point where IoT devices connect, learn, adapt, and interact intelligently.
How IoT Works
The following four elements are integrated into an IoT ecosystem to operate effectively.
- Sensor and devices
- Connectivity
- Data processing
- Actionable outputs
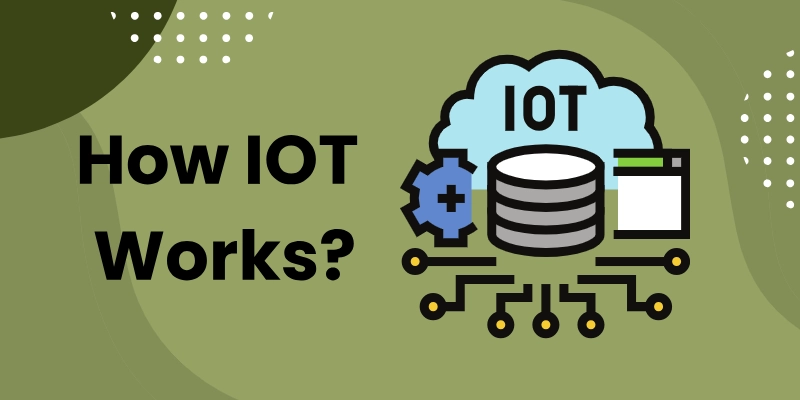
Sensors and Devices:
An IoT ecosystem includes smart devices connected to the internet. These devices have built-in systems like processors, sensors, and communication tools to gather, send, and respond to data from their surroundings.
Connectivity:
IoT devices can talk to each other through the internet. They send sensor data to an IoT gateway, which works as a central hub. Before sharing the data, it can be sent to an edge device where it is analyzed locally.
Data Processing:
Only important data is used to find patterns, give advice, and spot problems before they get worse. Analyzing data locally cuts down on the amount of data sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth.
Sometimes, devices talk to each other and act based on the information they share. Most of the work is done automatically, but people can still set them up, give instructions, or view the data. The way these devices connect and communicate depends on the specific IoT application.
Graphical User Interface
A graphical user interface (UI) is often used to manage IoT devices. For example, a website or mobile app can be the UI to control, register, and manage smart devices. These interfaces make it easier for users to interact with and monitor their devices.
IoT Architecture
IoT operates through a multi-layered architecture:
- Perception Layer: Collects data using sensors.
- Network Layer: Transfers data to processing units.
- Processing Layer: Analyzes data to derive insights.
- Application Layer: Interfaces with users, such as through mobile apps.
For instance, in smart agriculture, sensors in fields detect soil moisture, the network transmits this data, and automated irrigation systems take action based on analysis.
Applications of IoT in Different Industries
The versatility of IoT means it touches nearly every aspect of our lives.
1. Healthcare: IoT powers wearable devices for heart rate monitoring and remote patient care. With real-time data, doctors can offer better diagnoses and treatment plans.
2. Agriculture: Smart farming uses IoT for precision agriculture—monitoring soil, weather, and crop health to optimize yields and reduce waste.
3. Smart Homes: From voice-controlled assistants to security cameras, IoT enhances comfort and safety at home.
4. Industrial IoT (IIoT): IoT improves efficiency in manufacturing, enabling predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization.
These applications highlight how IoT is reshaping industries for the better.
Benefits of IoT in Everyday Life
IoT is a game-changer for modern living, providing convenience and efficiency. Imagine waking up to a home that automatically adjusts the lights, brews your coffee, and sets the perfect room temperature. That’s IoT making your day smoother before it even begins.
Improved Convenience:
IoT integrates seamlessly into daily routines, reducing manual tasks. Smart home devices like voice-activated assistants (e.g., Alexa, Google Assistant) make controlling appliances as easy as speaking a command. Outside the home, IoT-enabled navigation systems reduce commute times by offering real-time traffic updates.
Enhanced Productivity:
IoT streamlines processes in workplaces and personal tasks alike. For instance, wearables track fitness goals, while connected devices in offices monitor energy usage and automate workflows. By removing repetitive manual tasks, IoT allows individuals and businesses to focus on more impactful work.
Challenges and Risks of IoT
Despite its benefits, IoT faces significant challenges. These obstacles range from security vulnerabilities to privacy concerns.
1. Security Concerns:
IoT devices are susceptible to cyberattacks due to their connectivity. Hackers can exploit weak points in smart devices, accessing sensitive data or disrupting operations. In 2016, for example, the Mirai botnet attack turned IoT devices into tools for a massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
2. Privacy Implications:
IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, raising concerns about how that data is stored and used. Mismanagement or unauthorized access to this data can infringe on personal privacy.
3. Interoperability Issues:
IoT devices from different manufacturers often lack standardization, leading to compatibility problems. A smart home system, for example, may struggle to integrate devices from multiple brands.
Addressing IoT Challenges
Overcoming these challenges requires innovation and regulation.
Advanced Security Protocols:
Encryption, secure firmware updates, and robust authentication systems can protect IoT devices. Companies must prioritize building security into devices from the ground up.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance:
Governments and industry leaders need to establish clear guidelines for IoT usage, focusing on data protection and interoperability standards.
Consumer Awareness:
Users must be educated about securing their IoT devices by changing default passwords, updating software, and using secure networks.

Future of IoT
The IoT landscape is evolving rapidly, with exciting advancements on the horizon.
1. Trends Shaping IoT:
- 5G Technology: Faster internet speeds and lower latency will expand IoT applications, making real-time device interaction smoother.
- AI Integration: IoT devices are becoming smarter, with AI enabling predictive analytics and autonomous decision-making.
2. Predictions for IoT Adoption:
IoT is expected to integrate with emerging technologies like the metaverse and digital twins. For example, digital twins create virtual replicas of physical objects, allowing for real-time monitoring and simulation in industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
IoT and Sustainability
IoT isn’t just about convenience; it’s also a tool for building a sustainable future.
Environmental Conservation:
IoT helps reduce waste by optimizing resource usage. Smart grids balance electricity supply and demand, while IoT-powered water management systems prevent wastage.
Smart Cities:
IoT enables efficient urban planning by managing traffic flow, reducing energy consumption, and improving waste collection systems. This leads to cleaner, more sustainable cities.
IoT’s Impact on Businesses
IoT opens up new business opportunities, driving innovation and efficiency.
New Business Models:
Subscription-based services, predictive maintenance, and automated customer support are examples of IoT-enabled models.
Successful IoT Businesses:
- Amazon: Smart assistants like Alexa redefine e-commerce and home automation.
- Tesla: IoT-integrated vehicles offer autonomous driving and over-the-air software updates.
Businesses that embrace IoT gain a competitive edge by improving operations and enhancing customer experiences.

Key IoT Technologies
IoT thrives on several core technologies that enable connectivity and data management.
1. Cloud Computing and Edge Computing:
Cloud computing provides scalable storage and processing power for IoT data, while edge computing ensures faster data analysis by processing information locally on devices.
2. Blockchain and IoT Integration:
Blockchain secures IoT networks by enabling transparent and tamper-proof data management. This combination is particularly useful in supply chain and healthcare applications.
IoT Standards and Protocols
Standardization is crucial for seamless IoT integration.
Common Standards:
- MQTT: Lightweight messaging protocol ideal for constrained devices.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): Designed for low-power IoT devices.
Importance of Standards:
Standardized protocols ensure interoperability, making it easier for devices to communicate and work together regardless of manufacturer.
Getting Started with IoT
Interested in implementing IoT for personal or business use? Here’s how to begin:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine what you aim to achieve—automation, cost savings, or enhanced efficiency.
- Choose the Right Platform: Platforms like AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Google Cloud IoT offer tools for device management and data analysis.
- Ensure Security: Implement robust security measures to protect data and devices.
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project to test feasibility before scaling up.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we interact with the world around us. By connecting devices and leveraging data, IoT enhances convenience, efficiency, and sustainability. While challenges like security and privacy remain, advancements in technology and regulatory frameworks are paving the way for a safer and more integrated IoT ecosystem.
As IoT continues to grow, it holds immense potential to revolutionize industries, improve everyday life, and shape a smarter, more connected future. Embracing IoT today means stepping into a world of infinite possibilities.
What Do You Think About the Internet of Things?
We’d love to hear your thoughts! Share your opinions, questions, or experiences with IoT in the comments below.
👉 Don’t forget to like, share, and follow for more tech insights!
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions that help clarify key concepts about the Internet of Things (IoT).
Examples include smart thermostats (like Nest), fitness trackers (like Fitbit), and voice assistants (like Amazon Echo).
IoT security varies by device and manufacturer. While some devices are highly secure, others are vulnerable to cyberattacks due to weak encryption or outdated software.
Certain IoT systems can function locally without an internet connection, but most rely on connectivity for full functionality.
IoT simplifies tasks, enhances productivity, and improves convenience whether it’s automating home lighting or enabling remote health monitoring.
Skills in programming, data analytics, networking, and hardware design are essential for IoT professionals.
Industries like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and logistics benefit greatly. IoT enables real-time monitoring, automation, and predictive maintenance in these sectors.
An IoT system includes sensors/devices, connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.), data processing, and a user interface to manage or interact with the system.
Sensors collect real-world data such as temperature, motion, or humidity, which is then used to make decisions or trigger actions within an IoT system.
Yes. Many IoT devices collect personal data, and without proper safeguards, this information can be accessed or misused by unauthorized parties.
IoT data is often stored in cloud servers or edge devices. Cloud storage offers scalability, while edge computing provides faster processing near the source.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





