How do Websites Work? Explained for Everyone
Published: 2 Jun 2025
Ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you visit a website like Google or Amazon? You type a web address, hit “Enter,” and within seconds, the website loads on your screen. But have you ever stopped to think about how websites actually work?

In this guide, we’ll break down how websites work in a simple, beginner-friendly way no tech jargon, just clear explanations.
What Is a Website?
A website is a collection of related web pages hosted on a server and accessible through the Internet as part of the World Wide Web. Each website has a unique address called a domain name (like www.example.com) and can contain content such as text, images, videos, and interactive features.
Types of Websites
- Static websites: Show the same content to every visitor.
- Dynamic websites: Change content based on user actions or data.
Key Components of a Website
Here are some of the key components that make up a website and help it function properly.
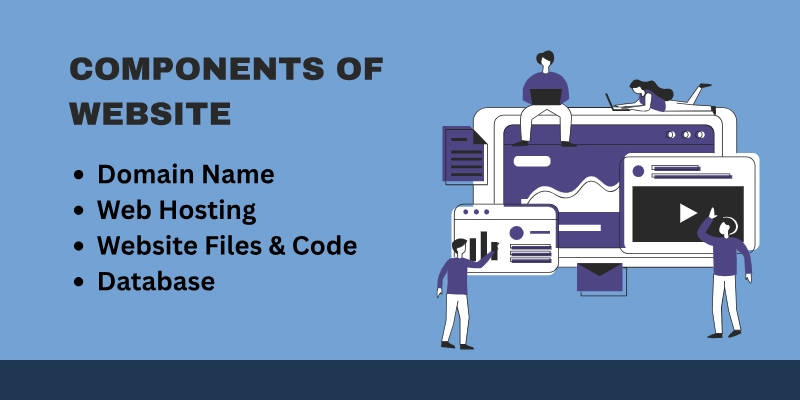
1. Domain Name
This is the address you type into your browser to visit a website. It’s easier to remember than a string of numbers (IP address).
Example: www.myportfolio.com
You register domain names through domain registrars like GoDaddy or Namecheap.
2. Web Hosting
Websites are stored on servers provided by web hosting companies. These servers deliver your website to visitors anytime, anywhere.
Types of Hosting:
- Shared Hosting
- VPS (Virtual Private Server)
- Dedicated Hosting
- Cloud Hosting
3. Website Files & Code
Websites are built with:
- HTML – for structure
- CSS – for design
- JavaScript – for interactivity
Many websites also use CMS platforms like WordPress, making it easier for beginners to create and manage websites without coding.
4. Database (for Dynamic Sites)
Dynamic websites store user-generated content, product listings, or blog posts in databases such as MySQL or MongoDB.
How the Web Works: Step-by-Step
Here’s a simple explanation of what happens when you open a website:
- You type a URL (e.g., www.example.com) into your browser.
- DNS Lookup: Your browser asks the Domain Name System to find the website’s IP address.
- Request Sent: The browser sends a request to that IP address via HTTP or HTTPS.
- Server Responds: The web server processes the request and sends back website files.
- Website Loads: Your browser reads the files and displays the website for you.
Client-Side vs Server-Side
- Client-side: Code that runs in your browser (HTML, CSS, JS).
- Server-side: Code that runs on the web server (PHP, Node.js, Python) to generate data and handle logic.
Frontend vs Backend
- Frontend = What users see: layout, buttons, images, and text.
- Backend = The behind-the-scenes logic: databases, login systems, and order processing.
Analogy:
- Frontend = Dining area (where you interact)
- Backend = Kitchen (where everything is prepared)
How Do Websites Stay Online?
To remain accessible 24/7, websites rely on the following:
- Reliable Hosting: Keeps the site live and available at all times.
- SSL Certificate: Ensures secure, encrypted browsing (HTTPS).
- Backups & Security: Protects data from malware, crashes, or hacking.
- CDNs (Content Delivery Networks): Boost loading speed by distributing content across multiple global servers.

What Makes a Website Work Well?
A successful website is more than just functional. It should be:
- Fast-loading
- Mobile-responsive
- Easy to navigate
- Secure with HTTPS
- Full of engaging, readable content
- Optimized for search engines (SEO)
Tools & Technologies Behind Websites

Common technologies used to build and manage websites:
Languages:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
- PHP
- Python
Content Management Systems (CMS):
- WordPress
- Joomla
Frameworks:
- React
- Laravel
- Django
Hosting Services:
- Bluehost
- HostItSmart
- Hostinger
Conclusion
Websites are the foundation of the internet, and now you know how websites work! From typing a URL to seeing the final page, there’s a complex system of technologies working together behind the scenes. Whether you’re a curious learner or planning to build your own site, understanding this process is the first step into the digital world.
Have questions or need help getting started? Drop a comment below or get in touch we’re here to support your web journey!
FAQs: How Do Websites Work?
Below are some important frequently asked questions (FAQs) that help clarify how websites work and what goes on behind the scenes.
A website is a collection of web pages stored on a server that people can access through the internet using a browser. It can contain text, images, videos, and interactive features.
A static website displays the same content to every visitor, while a dynamic website changes based on user input, location, or data from a database.
Not necessarily. Tools like WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace allow you to build websites without writing code. However, learning HTML, CSS, and JavaScript gives you more control and customization options.
A domain name is your website’s address on the internet (e.g., www.mywebsite.com). It helps users find your website easily without remembering its IP address.
Web hosting is the service that stores your website’s files on a server so they can be accessed online. Without hosting, your site wouldn’t be available to visitors.
When you enter a website address, the browser:
- Looks up the domain name’s IP address via DNS
- Sends a request to the web server
- Downloads the site’s files
- Displays them in the browser window
The frontend is the part of the website users interact with (design, buttons, layout), while the backend handles the data, server logic, and database interactions behind the scenes.
No. HTTPS encrypts the data between your site and its visitors. Without it, sensitive information like passwords or credit card numbers can be exposed.
A user-friendly website is fast, mobile-responsive, easy to navigate, secure, and provides clear, engaging content that meets the visitor’s needs.
Developers use a variety of tools including:
- Programming languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- CMS platforms (WordPress, Joomla)
- Frameworks (React, Django)
- Hosting services (Bluehost, Hostinger)

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks